Abstract
Background: The NIH-sponsored observational study "Comparative Study of Haiti and Miami Cohorts of Sickle Cell Disease CSHSCD" (R01HL149121) coordinates the follow up of children with sickle cell disease (SCD) in Haiti and compares it to a Miami cohort of children of either Haitian or African American ethnicity for the purpose of assessing barriers through questionnaires and examining differences in the care received in their respective environments.
Methods: Children less than 6 years of age with SCD are eligible for enrollment in five participating sites: University of Miami (UM, Miami, Florida), Hôpital Saint Damien (HSD, Tabarre, Haiti), Hôpital de l' Université d'Etat d'Haïti (HUEH, Port-au-Prince, Haiti), Hôpital Universitaire Justinien (HUJ, Cap Haitien, Haiti), and Hôpital Sacré Coeur (HSC, Milot, Haiti).
Medians and interquartile ranges or percentages were compared at baseline regarding demographics, clinical and growth parameters, laboratory tests, and the children's hydroxyurea (HU) utilization during the first year of enrollment (May 25, 2020-May 24,2021). A Likert-scale barrier questionnaire was distributed at baseline to assess differences in healthcare access. A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant to establish differences.
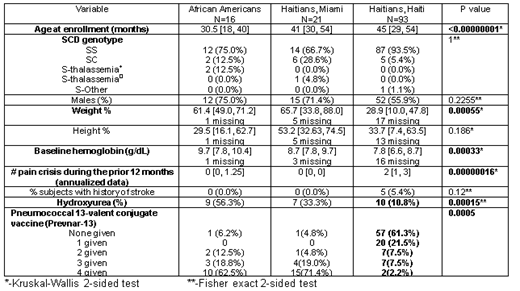
Results: 130 children were enrolled during the reported period. Significant differences were observed in age, weight percentiles, hemoglobin levels, pain rates, HU treatment, and pneumococcal vaccination.
Penicillin prophylaxis was always given by oral route in Miami, but only 39.8% times in Haiti, with 58% of children receiving prophylaxis by intramuscular injection every month and 2.2% (N=2 children) with either unknown or not receiving prophylaxis. Previous medication outsourcing accounted for the oral tablet form in Haiti. Parents in Haiti had more barriers regarding not able to afford treatment (21.5% compared to 8.1% in Miami) and had similar responses regarding not able to afford coming to clinic (21.5% vs. 18.9%). Parents in Miami expressed living far away from clinic (70.2% compared to 25.8% in Haiti), but had more help from other family members (78.4% vs. 33.3%). Interestingly, parents in Miami did not know sometimes what to do when the child was sick (40% respondents vs. 11% in Haiti). There were no major differences between the responses from the African Americans and Haitians living in Miami, except for not knowing sometimes what to do when child is sick (African-Americans having less doubts than Haitians; 25% vs. 52.6%). In short-term follow up, no enrolled children died, although two eligible children in Haiti died before enrollment. One child developed COVID-19 in Miami with only mild symptoms, which resolved.
Conclusion: At entry children in Haiti are older, weigh less, are more anemic, have more pain episodes, and fewer receive hydroxyurea treatment. Under-vaccination with pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (Prevnar-13) is notable in Haiti. There were significant differences detected on the barrier questionnaire among respondents in both countries.
Acknowledgment: We acknowledge NHLBI for supporting this work.
Alvarez: GBT: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Forma Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.